Difference between revisions of "Fibs and Facts"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "Fibonacci and Factorial are two of the basic examples for functional programming languages. Here we show their implementation in Wu. == Fibonacci == fib n = (> 2 n) 1 (+ 1...") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
fib n = (> 2 n) 1 (+ 1 (+ (fib (- n 1) (- n 2)))); | fib n = (> 2 n) 1 (+ 1 (+ (fib (- n 1) (- n 2)))); | ||
linfib x y n = (== 0 n) y (linfib y (+ x y) (- n 1)); | linfib x y n = (== 0 n) y (linfib y (+ x y) (- n 1)); | ||
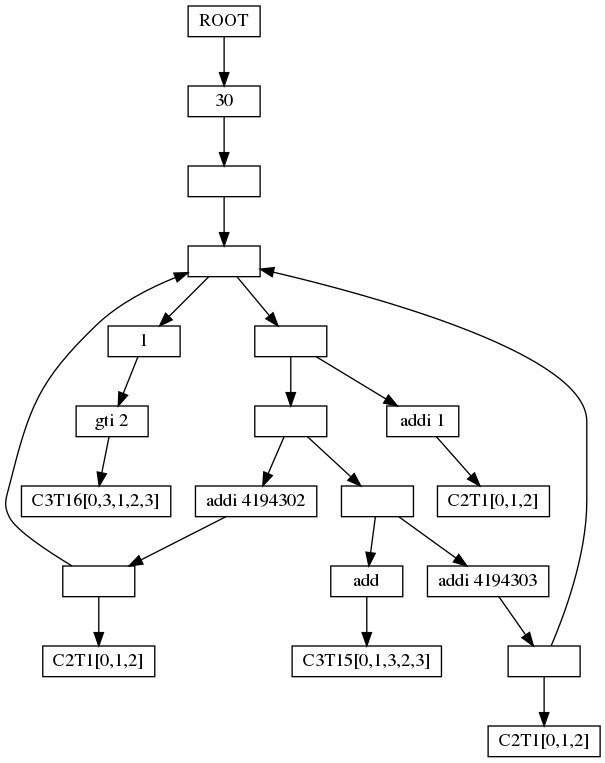
| + | |||
| + | [[File:fib.png]] | ||
== Factorial == | == Factorial == | ||
fact n = (> 2 n) 1 (* n (fact (- n 1))); | fact n = (> 2 n) 1 (* n (fact (- n 1))); | ||
| + | or, | ||
fact n = foldr + 0 (range 1 n); | fact n = foldr + 0 (range 1 n); | ||
Latest revision as of 12:43, 3 May 2022
Fibonacci and Factorial are two of the basic examples for functional programming languages. Here we show their implementation in Wu.
Fibonacci
fib n = (> 2 n) 1 (+ 1 (+ (fib (- n 1) (- n 2)))); linfib x y n = (== 0 n) y (linfib y (+ x y) (- n 1));
Factorial
fact n = (> 2 n) 1 (* n (fact (- n 1)));
or,
fact n = foldr + 0 (range 1 n);